Religious OCD Treatment without Medicine
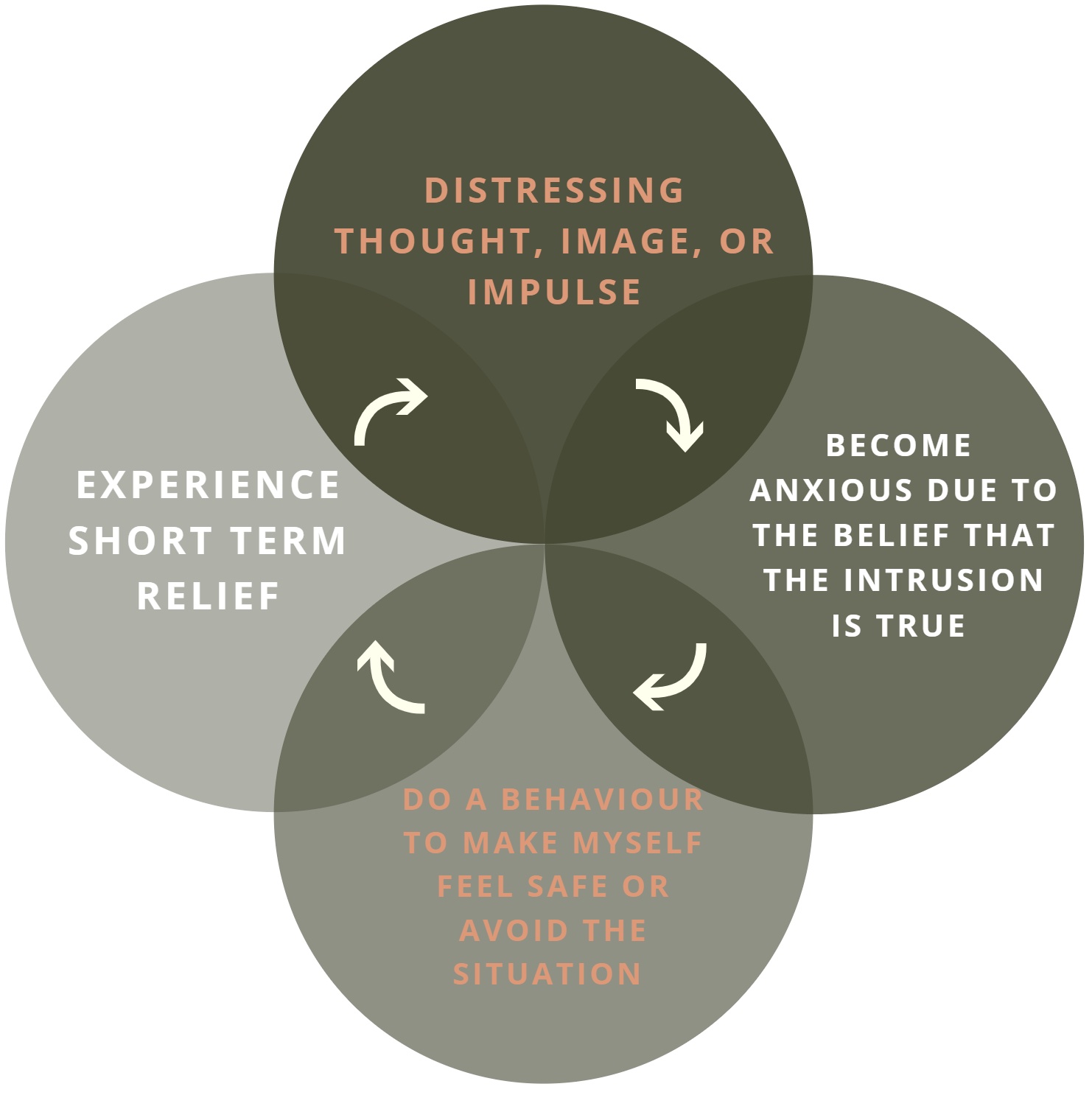
Religious OCD Treatment without medicine, also known as Scrupulosity, is a subtype of obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD) where an individual experiences excessive religious or moral concerns. This condition causes distressing, intrusive thoughts that revolve around religious practices, beliefs, or moral integrity, leading to compulsive behaviors aimed at alleviating anxiety.
It involves persistent and unwanted thoughts, doubts, or fears about religious matters. Individuals suffering from this condition often struggle with the fear of committing blasphemy, sinning, or failing to meet religious standards. This distress results in compulsive rituals, such as excessive praying, seeking reassurance from religious authorities, or engaging in repeated confessions. While faith and spirituality provide comfort to many, Religious OCD distorts them into sources of chronic anxiety.
Differentiating Religious OCD from Genuine Faith Concerns
It is important to distinguish between Religious OCD and sincere religious devotion. True faith typically brings peace, purpose, and fulfillment, while Religious OCD is characterized by distress, anxiety, and an overwhelming fear of wrongdoing. Unlike genuine devotion, which allows for flexibility and grace, Religious OCD imposes rigid, perfectionistic standards that can make religious practice a source of distress rather than comfort.
Symptoms of Religious OCD Treatment without Medicine
- Repetitive prayers or rituals beyond what is necessary or customary.
- Constant self-monitoring for sinful thoughts or actions.
- Seeking reassurance from religious leaders, family, or friends.
- Avoiding religious practices for fear of doing them incorrectly.
- Excessive fear of divine punishment or spiritual failure.
- Re-reading religious texts repeatedly to ensure proper understanding.
Physiological and Psychological Impact
Physiological Impact
Chronic stress and anxiety can result in fatigue, muscle tension, headaches, and digestive problems. Sleep disturbances are also common due to persistent intrusive thoughts.
Psychological Impact
Feelings of guilt, shame, and extreme self-doubt often lead to emotional distress. Individuals may experience depression, social withdrawal, and difficulty maintaining healthy relationships. The overwhelming nature of these obsessions can also impair concentration and decision-making abilities.
Types of Religious OCD
- Blasphemous Thoughts OCD: Unwanted and distressing thoughts about religious figures, sacred texts, or rituals. Examples include sexual thoughts about deities, doubts about God’s existence, or intrusive images considered blasphemous.
- Moral Scrupulosity: Excessive concern over being perfectly moral or ethical in every action.
- Purity OCD: Fear of spiritual contamination, leading to excessive cleansing or rituals.
- Prayer OCD: Repetitive or prolonged prayers due to fear of not doing them correctly.
- Confession OCD: Frequent need to confess minor or nonexistent sins to seek absolution.
- Religious Avoidance OCD: Avoidance of religious settings or practices due to fear of performing them incorrectly.
Causes of Religious OCD
- Perfectionism: A desire to follow religious teachings flawlessly can trigger obsessive fears.
- Upbringing: Strict religious environments emphasizing punishment may contribute to excessive guilt and fear.
- Fear of Consequences: The belief that even a small mistake may lead to severe outcomes fuels compulsions.
- Cognitive Patterns: Black-and-white thinking makes individuals view their actions as entirely right or wrong.
- Stress and Life Changes: Major transitions, trauma, or stressors can trigger obsessive concerns.
How to Overcome Religious OCD Treatment without Medicine
Understanding the Nature of Thoughts
- Recognize that intrusive thoughts are automatic and do not define one’s faith or morality.
- Accept thoughts without engaging in compulsive behaviors.
Cognitive Techniques
- Identify unrealistic beliefs and replace them with balanced perspectives.
- Practice self-compassion instead of self-criticism.
Behavioral Strategies
- Gradually reduce compulsions through exposure exercises.
- Engage in religious practices mindfully rather than excessively.
Mindfulness and Relaxation
- Incorporate deep breathing and meditation to lower anxiety.
- Focus on the present moment instead of hypothetical fears.
Seeking Professional Help
Work with a therapist trained in CBT and ERP to address intrusive thoughts and compulsive behaviors effectively.
Case Study: Overcoming Religious OCD Concerns
Client: Mr. S | Duration: 2+ Years
Fear of Saying or Thinking Offensive Words Against God: Mr. S had distressing intrusive thoughts of offending his deity. Through therapy, he learned to see these as harmless mental events and stopped apologizing repeatedly.
Fear of Being Cursed for Actions or Thoughts: He believed certain thoughts or actions could bring divine punishment. With cognitive restructuring, he learned to reject these fears and no longer obsesses over them.
Fear That Mistakes in Worship Will Lead to Punishment: He feared that mispronouncing a mantra would anger the deity. Therapy helped him accept human imperfection and stop reassurance-seeking.
Compulsive Apologizing to the Deity: Mr. S repeatedly apologized for intrusive thoughts. He learned to stop these rituals and trust that intention matters more than repetition.
Fear of Losing Artistic Skills as Punishment: He believed his talents were dependent on divine favor. Therapy helped him realize his creativity is innate, not conditional.
Fear That Daily Tasks Done with Bad Thoughts Bring Harm: He once repeated tasks like closing doors to neutralize negative thoughts. Now, he performs them normally without distress.
Fear That Masturbation Offends God: He felt guilt over natural acts, viewing them as sinful. He learned this belief was irrational and that sexuality is a normal biological process.
Fear That Not Following Rituals Properly Will Bring Harm to Family: He feared that improper blessings would harm his loved ones. He has now stopped ritualistic repetition and acts naturally.
Excessive Seeking of Blessings from God: Previously, he bowed excessively, fearing loss of divine favor. Now, he practices balanced worship twice daily without anxiety.
Fear That Thoughts Alone Can Lead to Sin: He believed that having bad thoughts was equivalent to sin. Therapy helped him realize thoughts are not actions.
Success Stories – Religious OCD Treatment without Medicine
Success Story 1 – Meera’s Journey to Freedom
Meera, a 27-year-old teacher from Delhi, battled Religious OCD for 8 years. She repeated prayers for hours out of fear of imperfection. With Emotion of Life’s CBT and ERP program, she learned to manage intrusive thoughts and trust herself. Today, she prays peacefully and lives free of OCD’s burden.
Success Story 2 – Arjun’s Recovery Journey
Arjun, a 21-year-old student from Pune, struggled with intrusive doubts and guilt about offending God. At Emotion of Life, daily ERP sessions helped him face fears without confessing. Within 4 months, he regained control over his faith and enjoys a calm, confident spiritual life.
Client Reviews
Priya, 30 (Bengaluru): “Emotion of Life’s daily therapy gave me the strength to stop compulsions. I finally feel free after years of fear.”
Ramesh, 35 (Hyderabad): “I tried medicines before, but nothing worked like ERP and CBT. Now I can pray peacefully without fear.”
Conclusion
Religious OCD Treatment without medicine is a challenging condition that distorts faith into anxiety. Understanding its symptoms and causes allows individuals to seek the right strategies for managing fears and compulsions. With structured therapy, mindfulness, and balanced practice, individuals can cultivate a healthy relationship with faith that fosters peace and spiritual well-being.
Call: +91 9368503416 www.emotionoflife.in Email: info@emotionoflife.in
Book Now | Review | OCD Types | Our Experts | Success Stories| Contact Us| MyPsychologist