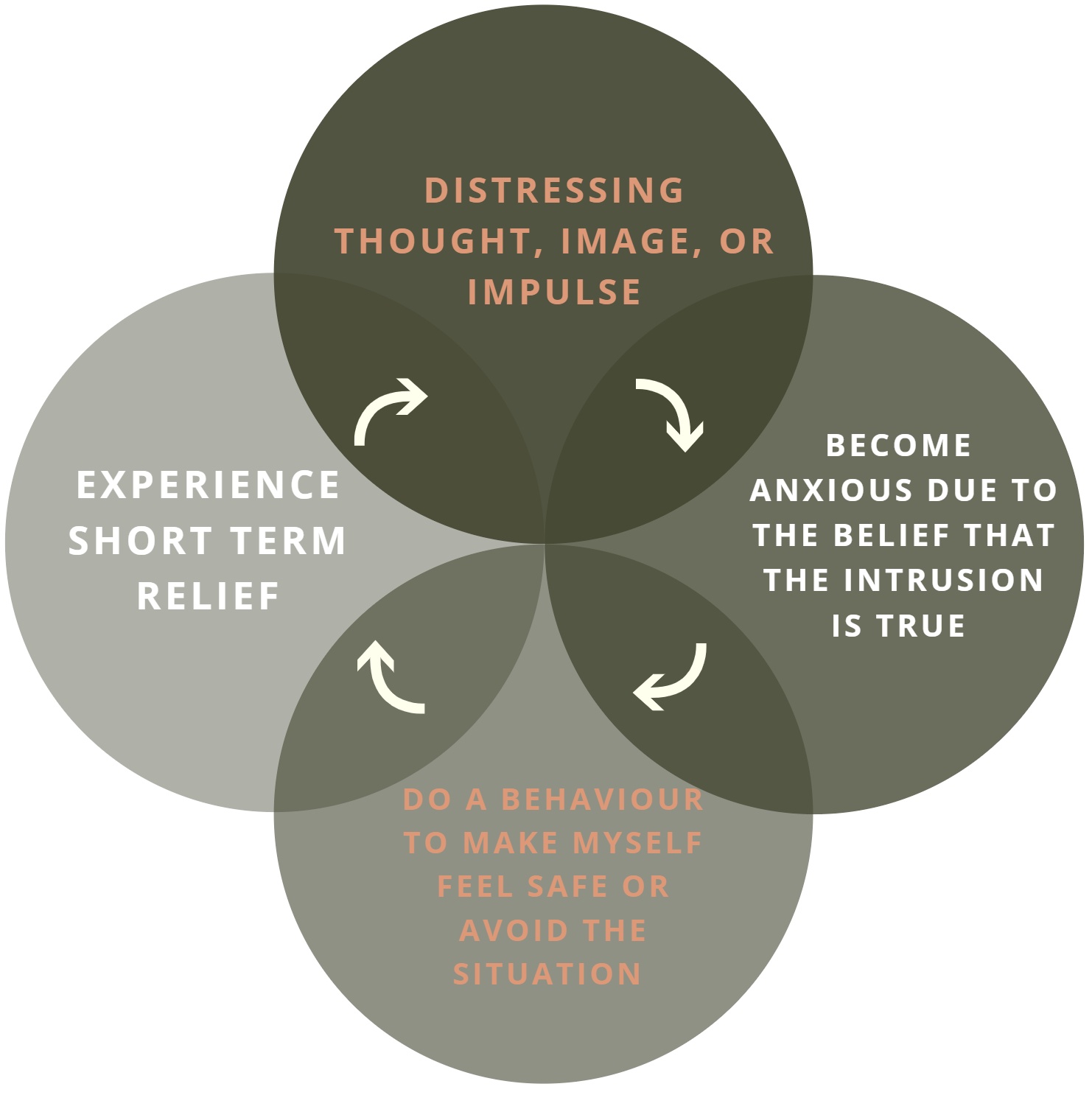
Mental Masturbation in OCD is an informal and non-clinical phrase that basically explains the feeling of stimulation that is generated by excessive thinking, but in reality, it leads to no actual growth or outcome. This phenomenon can include over-analysing basic ideas, theories, or problems. The repeated thinking process that goes in a loop with no real solution being executed. People who fall in this process enjoy the feeling of thinking and going in loops rather than putting into use the actual outcome or conclusion. Hence, nothing productive is actually achieved by the end of this rumination. In OCD, Mental Masturbation in OCD is referred to as the repetitive and stimulating thinking that would feel like working on the problem, but in reality is a mental compulsion. Although this is not a clinical term, it can be correlated with rumination, mental compulsion, and mental reassurance. It usually involved repeatedly analysing the same fear and outcome, with no actual overcoming, trying to figure things out perfectly, in a way that feels “good”, mentally arguing, debating, proving a point to oneself, and constantly having an urge to find relief and certainty inside one’s mind. For example, a person thinking about whether they have locked the door correctly, they will keep thinking about it in an ongoing loop, trying to find out mental proofs and cues to eventually have the certainty of having done it correctly. And after this, although they feel sure, this surity doesnt seem to last long.
Manifestations of Mental Masturbation in OCD
This practice of mental masturbation in OCD manifests in three major ways. The first one is through the actual symptoms, including constant mental loops around the same topic and being unable to stop these thoughts once they get triggered. Getting temporary relief, which is again followed by anxiety, leads to mental exhaustion and brain fog. Mental Masturbation in OCD further leads to hampered concentration and decision-making, and then an increased urge to get mental reassurance yet again. Another area is the physiological changes that include increased heart rate, muscle clenching, shallow breathing, and restlessness. This also includes an increase of stress hormones, a weakened digestive system, sleep disturbances, headaches, and weakened energy levels. Lasty it affects us psychologically in terms of less tolerance to uncertainty, over-reliance on our thoughts to cope with any given situation, reduced trust in our intuition and memory, the fusing of thoughts and actions leading to less differentiation between the two, causing even more stress. This can trigger feelings like anxiety, shame, frustration, and helplessness. All this can lead to avoidance behaviours, less engaement on real-life activities, dependence on thoughts and reassurance.
Types of Mental Masturbation in OCD
Mental Masturbation in OCD can have many types depending on what the mind is trying to get relief from.
- Rumination – In this type of mental masturbation, there is endless thinking about why the thoughts came in, and the feeling that if it is analysed properly, it will go away, but that never happens. This keeps the mind stuck in a loop.
- Mental-reassurance – This means internally telling yourself “it’s okay”, “I’m fine”, etc in order to get peace. These statements are repeated in a loop to create a false perception of calmness for a temporary moment. This temporary feeling of relief from mental masturbation strengthens OCD.
- Mental-checking – In this form of Mental Masturbation in OCD, the person keeps on going in a loop of thinking whether they have done something or not. For example – Did I do this? Was my intention bad? Did I enjoy doing this? etc. This is commonly seen in Harm OCD and Relationship OCD.
- Moral Reasoning – In this subtype, the person constantly keeps thinking about right and wrong, good or bad, moral or immoral. They will keep replaying their actions in their mind to check if it was good or bad. This over-involvement leads to them questioning their ethics, character, and responsibility. Hence, making their mind a courtroom.
- Thought neutralization – This form of mental masturbation in OCD refers to replacing a “bad” thought with a “good” one. Basically, mentally undoing a thought that comes to mind by repeating phrases, numbers, or images.
- Predictive thinking – This aspect of Mental Masturbation in OCD refers to the “What-if” thoughts that keep the person stuck in a loop. Leading to a future-focused catastrophising habit.
Causes of Mental Masturbation in OCD
1. Psychological Causes Mental Masturbation in OCD
- Intolerance of uncertainty: Strong need to feel completely sure, leading to repeated thinking to remove doubt.
- Inflated responsibility: Belief that failing to think things through could cause harm.
- Thought–action fusion: Interpreting thoughts as dangerous or meaningful, increasing fear of thinking itself.
- Perfectionism: Need for “correct” or morally perfect thoughts, causing endless analysis.
- Emotional avoidance: Thinking is used to escape anxiety, guilt, or discomfort instead of feeling it.
2. Social Causes of Mental Masturbation in OCD
- Reassurance patterns: Repeated reassurance from others (or self) reinforces thinking as a coping strategy.
- Moral or cultural pressure: Strong emphasis on being right, good, or responsible increases self-monitoring.
- Learned behavior: Growing up in environments where overthinking and worry are modeled.
- Stigma around emotions: Difficulty expressing anxiety leads to internal mental coping.
3. Environmental Causes in Mental Masturbation in OCD
- Chronic stress: Academic, work, or relationship stress keeps the nervous system in threat mode.
- Unpredictable environments: Lack of structure increases the need for mental control.
- Overexposure to information: Constant analysis, checking, and comparison reinforce rumination.
- Isolation: More time alone increases inward focus and repetitive thinking.
Management and Treatment of Mental Masturbation in OCD
At Emotion of Life, the focus is on non-medication-based recovery using structured psychological interventions:
1. Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT)
CBT will identify mental masturbation in OCD as a compulsion, not problem-solving. This helps to learn that repeatedly analyzing thoughts does not bring clarity but strengthens OCD. Cognitive restructuring reduces beliefs like “I must think this through to be safe.”
2. Exposure and Response Prevention (ERP)
ERP is the gold standard treatment for mental masturbation. It involves allowing intrusive thoughts to be present without engaging in mental analysis, reassurance, or checking. By preventing mental responses, the brain learns that anxiety reduces on its own without thinking.
3. Acceptance and Commitment Therapy (ACT)
ACT teaches acceptance of uncertainty and discomfort. Instead of fighting thoughts, it helps to make people learn to let thoughts exist while choosing meaningful actions, weakening the habit of compulsive thinking.
4. Mindfulness-Based Strategies
Mindfulness helps observe thoughts without getting involved. The goal is not to stop thoughts, but to notice them and return attention to the present, reducing automatic rumination.
6. Family Education & Support
Educating family members prevents reassurance-giving, which unintentionally reinforces mental compulsions. Support focuses on encouraging tolerance of uncertainty.
Success Stories
1. Nitish, 28, Pune:
Nitish was washing his hands 100+ times a day, unable to touch his own furniture without gloves. After joining the 90-day OCD Recovery and Cure Program, his handwashing reduced to normal hygiene levels. Today, he works confidently in an IT company.
2. Meera, 29, Mumbai:
Meera struggled with religious and moral rumination, spending hours mentally reviewing prayers and intentions. Therapy helped her accept uncertainty and practice non-engagement with compulsive thinking. She now practices her faith with calmness instead of fear.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) on Mental Masturbation in OCD
1. Is mental masturbation the same as overthinking?
No. While overthinking can be normal, mental masturbation in OCD is compulsive and anxiety-driven. It is done to gain certainty or relief, and keeps repeating without gaining any outcome or relief.
2. Why does mental masturbation feel necessary or helpful?
It provides temporary relief from anxiety. The brain learns that thinking reduces discomfort, so it keeps repeating the behavior, even though it worsens OCD in the long-term.
3. Can mental masturbation in OCD happen without visible compulsions?
Yes. In Pure-O OCD, mental masturbation may be the main compulsion, making OCD harder to recognize because everything happens internally.
4. Should I try to stop my thoughts completely?
No. Recovery does not involve stopping thoughts. It involves not engaging, analyzing, or reassuring when thoughts arise and allowing uncertainty to exist.
5. How long does it take to reduce mental masturbation with treatment?
With consistent ERP-based treatment, many people notice improvement within weeks. Long-term recovery depends on practicing response prevention regularly and reducing reassurance.
Emotion of Life’s Unique Holistic 360 Therapeutic Approach for OCD Recovery and Cure Program
The approach is highlighted in the 16 steps.
- Initial discussion over the call, then consultation for needs assessment on video call
- Comprehensive Psychological Assessment to understand the OCD pattern
- Development of the scope of work as the Problem Statement shared by the client and caregiver
- Therapy foundation Course, which includes Therapy preparedness, 27 OCD success mantras, and cognitive restructuring
- Written Consent for opting OCD Recovery & Cure Program
- Developing the Monitoring & Evaluation Framework after the first 2 weeks
- Execution of CBT and ERP Customized Therapy session
- Family Therapy Sessions (weekly)
- Progress Monitoring (Monthly)
- Mid-Term Evaluation (After 2 months) for course correction, if any
- Review of OCD Recovery status at 4-months.
- Relapse Management in the 5th month
- End-Term Evaluation to ensure all recovery milestones are achieved
- Termination of Sessions
- Weekly follow-up (up to next 6 months) to ensure no relapse
- Declaration of Cure state after successful 6 months follow-up.
Conclusion
Mental masturbation in OCD is a subtle yet very strong form of mental compulsion that keeps individuals entangled in loops of anxiety and self-doubt. Although it appears as problem-solving or deep thinking, it actually functions as a safety behavior aimed at achieving certainty and emotional relief. Over time, this pattern strengthens OCD, increases distress, and reduces trust in one’s own experiences. Understanding mental masturbation in OCD as a learned response rather than a personal weakness is essential for recovery. Effective treatment focuses on changing how one responds to intrusive thoughts, not on eliminating them. Approaches such as CBT, ERP, ACT, and mindfulness help individuals escape the loop of excessive mental analysis and build tolerance for uncertainty. With consistent practice, supportive environments, and healthy lifestyle habits, individuals can regain control over their attention and reconnect with meaningful life activities. True progress occurs when thinking is no longer used to manage fear, allowing the mind to become calmer and more flexible over time.
At Emotion of Life, under the leadership of Shyam Gupta (OCD Specialist Therapist & Rehabilitation Psychologist) and Pratibha Gupta (Psychologist & Counsellor), clients from across India and globally recover from OCD without medicine, using evidence-based therapies such as CBT and ERP.
Remember: recovery is possible.
Call now: +91 9368503416
Website: www.emotionoflife.in
Email: info@emotionoflife.in
Book Now. | Recover Client Review | OCD Types | Meet Our Experts | Success Stories| Contact Us| MyPsychologist